OECD releases detailed study of global education trends for 2014
The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has released its annual Education at a Glance report for 2014, and it is full of useful trend information and other background for international educators. The publication covers educational data spanning 34 OECD countries as well as the following non-OECD states: Brazil, Russia, Argentina, China, Colombia, India, Indonesia, Latvia, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. The broadest finding is that it is becoming more typical for the world’s students to attain at least secondary education and more common for them to pursue tertiary education as well. Younger adults are more likely to achieve higher levels of education than their older counterparts, especially in emerging markets. We will look at this trend briefly in the next section of this article. But our main focus will be international student mobility trends. The publication documents enormous growth in the numbers of students studying abroad from 1975 to 2012 – particularly in the time span 2000–2012. Moreover, it reveals new trends in mobility, including the growing importance of intra-regional mobility and new or emerging destinations for international students.
Pursuing higher levels of education becoming the norm
Education at a Glance 2014shows that roughly 8 in 10 younger adults (aged 25–34) in the survey countries have completed upper secondary education, (i.e., education that allows them access to tertiary education and expanded labour market opportunities). As for tertiary education, attainment levels are relatively lower (roughly 3 in 10 adults have achieved a tertiary-level education) but they have risen by 10% across the OECD countries since 2000. Younger adults are generally more likely to have a tertiary education (40%) than older adults (25%), and in some countries, generational gaps are particularly striking. In South Korea, the gap is 52 percentage points between adults aged 25–34 who have completed tertiary education as compared to those aged 55–64. Wide gaps like these attest to the dramatic expansion of higher education capacity in recent years – and appetite for tertiary education – in many countries. The report estimates that 58% of young adults in OECD countries will enter university-level programmes in their lifetimes, and that 18% will enter vocational programmes.
International mobility trends
In 2012, more than 4.5 million students were studying abroad at the post-secondary level – more than five times the number of students abroad in 1975. The average annual growth rate in international student mobility between 2000 and 2012 was 7%.
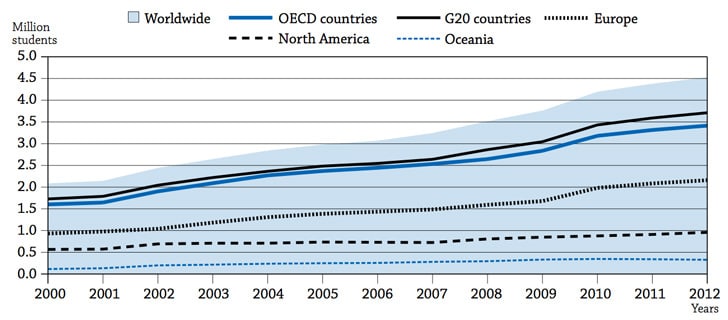
- The countries with the highest proportions of international students in their overall enrolments (more than 10%) are Australia, Austria, Luxembourg, New Zealand, Switzerland, and the UK.
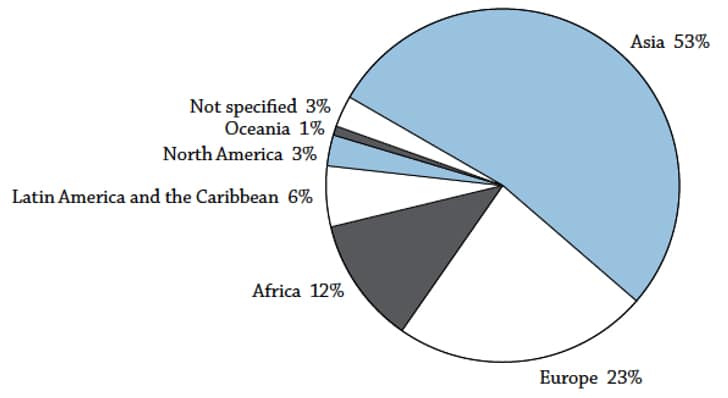
- Asia is the source for more than half of today’s internationally mobile students (53%), with China, India, and South Korea the main source countries.
- G20 countries host 82% of all foreign students, and 75% study in OECD countries.
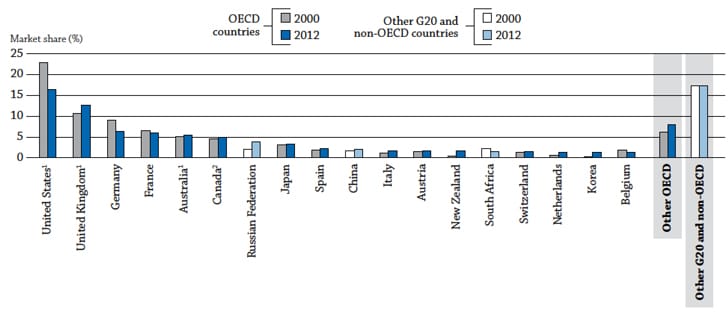
- Collectively, the US, Canada, the UK, France, Germany, and Australia host more than half of the students studying abroad today.
- Europe is the top regional destination, claiming 48% of internationally mobile students. North America follows with 21%, and then Asia with 18%.
- New destinations are commanding a higher and higher share of international students, while some traditional leaders are losing share (e.g., the share for the US dropped from 23% in 2000 to 16% in 2012). The Oceania region as well as Latin America, Africa, and the Caribbean are cited by the report as emerging destination regions.
- OECD countries receive far more international students than they send out. The report notes, “In 2012, the number of foreign students enrolled in tertiary education in OECD countries was, on average, three times the number of students from OECD countries studying abroad.”
- The language of students is a major influencer in where they choose to study abroad, and the current global dominance of English as a language of business/communication is thus a significant factor in the share of international student mobility held by English-speaking destination countries. “The prevalence of predominantly English-speaking destinations, such as Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States, in part reflects the progressive adoption of English as a global language. It may also reflect the fact that students intending to study abroad are likely to have learned English in their home country or wish to improve their English-language skills through immersion in a native English-speaking context.”
- Other important drivers of mobility cited in the report include: tuition fees (and intra-regional policies on this, for example, EU countries providing tuition fees as low as those charged to domestic students for international students from other EU countries); quality of programmes (with more and more attention being paid to international rankings of institutions); and immigration policies.
The importance of regions
Education at a Glance 2014notes a continuing trend towards intra-regional mobility around the world:
“Global student mobility follows inter-and intra-regional migration patterns to a great extent. The growth in the internationalisation of tertiary enrolment in OECD countries, as well as the high proportion of intra-regional student mobility show the growing importance of regional mobility over global mobility. Student flows in European countries and in Eastern Asia and Oceania tend to reflect the evolution of geopolitical areas, such as closer ties between Asia-Pacific countries and further co-operation among European countries beyond the European Union.”
The OECD also highlights the following as the main reasons students will travel beyond their home regions for study abroad:
- The destination country is a leading and/or traditional location for study abroad (e.g., the US and UK). Their established reputations and international education infrastructures are well known and they have significant numbers of institutions on international rankings lists such as the QS.
- The destination country has historic, cultural, or language ties with other countries, making it attractive to prospective international students interested in these (e.g., Spain and Portugal).
But, the report says, a destination country’s proximity to source countries – and associated marketing and policies (e.g., tuition, immigration) – is increasingly a factor in international students’ decisions as to where to study abroad. So:
“A large proportion of foreign students in OECD countries come from neighbouring countries. In all OECD countries in 2012, an average of 21% of all foreign students came from countries that share land or maritime borders with the host country. Higher levels of mobility from neighbouring countries are not only the result of being in a particular geographic situation, as in the Czech Republic, but may also reveal cost, quality and enrolment advantages that are more apparent to students in neighbouring countries.”
Europe is a prime example of the importance of region in international student mobility trends. As we reported earlier this year:
“Europeans account for nearly a quarter of all internationally mobile students and mobility in Europe, and the number of international students in Europe increased by 114% from 2000 to 2010.”
Not coincidentally, Europe has been proactive in its policies to leverage regional mobility flows, for example the EU’s 2013 approval of a major expansion of the Erasmus progamme (now Erasmus+). For further examples of emerging patterns of intra-regional mobility, see also our recent reports on Europe, sub-Saharan Africa, and Southeast Asia. With the emergence of regional education hubs such as China and Malaysia, coupled with continuing growth in demand for tertiary education across Asian markets, we can no doubt expect the global share of international students hosted within this key region to continue to grow over the years ahead.
















