Are China’s outbound student flows about to peak?
- A new analysis argues that key demand drivers for Chinese outbound are weakening, with the end result that the number of Chinese students going abroad will peak and possibly decline within the next five years
China has been an important driver of global growth in international student mobility for decades. As of 2020, Chinese students continued to account for a significant share of foreign enrolment in the world's top study destinations – ranging from roughly a quarter of all international students in Canada to nearly 40% of the foreign enrolment base in both the United States and Australia.
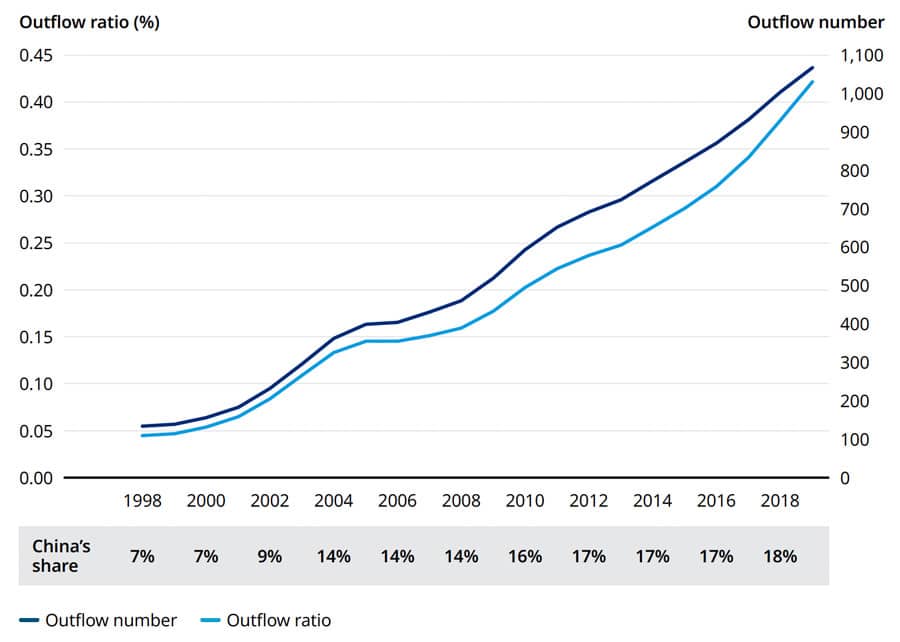
But there have been signs for some years now of slowing growth in Chinese outbound. And the profound disruption of the pandemic, along with an apparent sluggishness in the recovery in Chinese numbers this year, has only contributed to the unease across the industry as to the future prospects for this key sending market.
A new analysis from international consultancy Oliver Wyman explores some of the factors that will shape Chinese outbound in the years to come, and concludes that an inflection point is near. As co-authors Claudia Wang and Monique Zhang sum up:
"We expect the total number of Chinese students in overseas higher education degree programs to peak within five years, and then enter a track of stagnation or even slight decline."
However, we have to be careful about our framing here. Even a slowing China is still a massive marketplace distinguished by continuing, strong demand for study abroad. As such, China and Chinese students will no doubt continue to figure prominently in the recruitment plans of international educators for the foreseeable future. But what the recent-year trends are telling us – and what the Oliver Wyman analysis underscores – is that Chinese outbound may no longer drive overall growth in student numbers to the extent that it has historically done.
Weakening demand drivers
The Oliver Wyman paper sets out that demand for study abroad is built around four types of demand factors: education drivers (notably a shortage of seats in high-quality higher education institutions at home); economic drivers (especially a salary premium tied to overseas degree attainment); country-specific factors (such as historical mobility patters, cultural links, or proximity to study destinations); and systematic drivers (globalisation, for example).
If we hold those key demand drivers up to the Chinese market, it is easy to imagine where some downward pressure might be coming from. "The world is heading in the direction of a new order, diverting from the path of globalisation that had previously been the norm for many years," note the authors. "China, in particular, has been more determined than ever to take measures to build up its national competitiveness in various aspects…Providing quality education is one of the priorities."
Indeed, over the last decade or two, we have seen an unprecedented expansion of higher education in China, both in terms of capacity and quality. There are many more university seats available to students in China today than was the case 20 years ago, including those on offer from an expanding tier of highly ranked Chinese institutions. This expansion has roughly paralleled the continued growth and power of the Chinese economy, which, by some measures, is now the world's largest. The knock-on effect of those inter-twining trends is that the premium associated with an overseas degree (in terms of salary and employment opportunities) is starting to fade.
"For Chinese students, the rewards of studying abroad, defined as the premium over studying in China, are gradually declining," explain the co-authors. "With the wage premium shrinking, tertiary education capacity constraints loosening, and access to international-quality education at home increasing, the only push factor remaining is the growing [population base that can afford to fund studies abroad]."
In a similar vein, a separate analysis undertaken by Times Higher Education points out a shift in post-graduate study trends over the last five years. THE explains that a study of graduate employment reports from China's ten top-ranked universities, "Indicates that the proportion of students enrolling with a foreign institution after graduation has declined across the board since 2017. At the same time, the number of graduates taking postgraduate courses at Chinese universities has increased significantly, reflecting the growing strength of domestic higher education provision as well as COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions."
Ms Wang and Ms Zhang pick up the political theme in their commentary and point to additional systemic factors as well: "Simultaneously, with the new geopolitical background, regulatory headwinds and government intervention are expected to further guide the development of the industry: The importance of English has been lessening throughout the K-12 education system; and traditional feeder schools, such as premium bilingual schools, are being consolidated and international curricula are no longer allowed at compulsory education stage."
The authors conclude that, in the face of flat or declining numbers from China, international educators will need to look to other significant sending markets – such as India, Vietnam, and Brazil – to continue to drive overall growth in international mobility into the future.
For additional background, please see:
















