Fifty-fold increase in English-taught bachelor’s degrees in Europe
From the turn of the century onward, Europe has seen dramatic growth in the number of English-medium programmes on offer throughout the 19 countries of the European Higher Education Area (EHEA). The Bologna Declaration, formally adopted by European ministers of education in 1999, has been an important catalyst. The Bologna Process established the EHEA, and with it the goal that students and graduates could move freely among member states, using qualifications earned in one country to meet the requirements of admission for further study in another.
The first wave of the expansion in English-taught programmes in Europe was largely concerned with master’s degrees (ETMs), which expanded in number from 725 in 2001 to more than 8,000 by 2014.
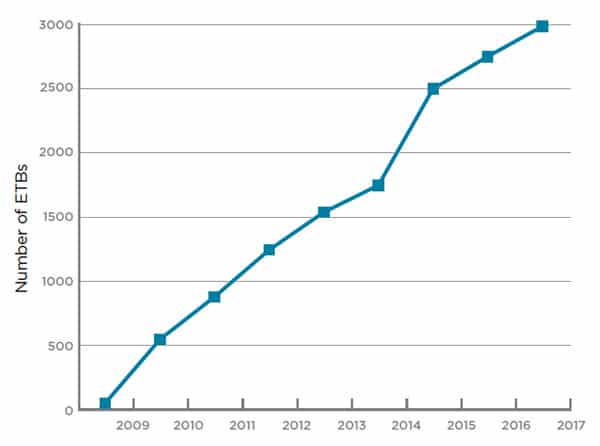
However, a new study from the European Association for International Education (EAIE) and StudyPortals highlights a second wave of expansion, but this time at the undergraduate level. In less than a decade, the number of English-taught bachelor’s programmes (ETBs) in the EHEA has grown from 55 in 2009 to just under 3,000 as of this year.
Strategic goals
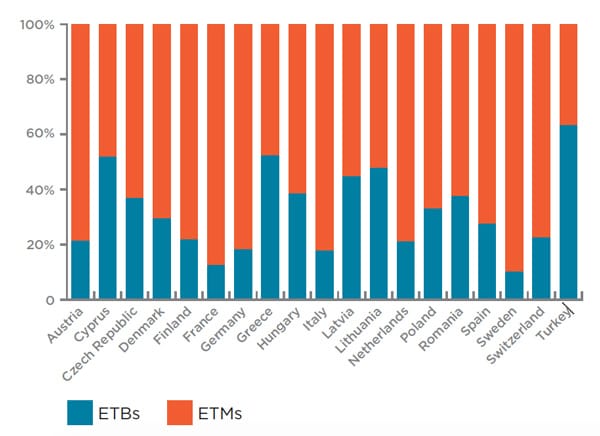
The EAIE/StudyPortals study finds that this proliferation of English-medium degree programmes in Europe is part of a broader internationalisation effort by European institutions. Most say they are adding English-taught degrees in order to boost internationalisation and institutional competitiveness, including the ability to attract international faculty and foreign students. There are underlying business goals here to be sure. Universities are adding English-taught degrees in order to generate tuition revenues from both local and visiting students, and institutions in all EHEA states charge tuition for non-EU students enrolled in foreign language-taught degree programmes. As the report notes, “Annual tuition fees for ETBs are, on average, highest in Switzerland (€20,942), followed by Sweden (€19,522) and France (€14,746). The more affordable ETBs in Europe are offered by Latvia (€2,819), the Czech Republic (€2,983) and Lithuania (€3,041). In some countries the averages can be skewed by a number of private and/or foreign providers charging comparatively high fees.” But these business goals are accompanied by the other benefits that often attend a growing foreign student body on any campus, including greater numbers of international faculty, improved English proficiency among the faculty, and more international exposure for local students. “Often beginning as mere translations of local-language programmes, ETBs have grown into distinct programmes catering to the needs of a diversified student population,” concludes the report. “This is, however, not a reality at every institution, as many struggle with English language and international pedagogical skills of staff, illuminating a need for additional training in this area. Many classrooms also still lack in diversity, thus limiting the international environment and learning potential of ETBs.” Going forward, many institutions see increasing student demand for English-taught programmes in Europe, and a future where English-medium programmes will continue to increase in number but will become more specialised over time as well.
The students’ view
This is not to say that there are not challenges ahead as well for many institutions in delivering English-taught programmes. These persist as well, especially in terms of the suitability of curriculum, the availability of English-speaking faculty, the adaptation and internationalisation of curriculum, and the level of English instruction for degree-bound students. At a more philosophical level: “Teaching in English has always been contested,” says a recent editorial in University World News. “First from a political point of view, with the argument that shifting from teaching in the local language to teaching in English may endanger the survival of the local language and culture.” The author, Hans de Wit, is quick to point out that this critique does not come from students, most of whom are happy for the opportunity to study in English. Instead he notes that, “The main opposition comes from faculty and organisations dealing with language policy, whose main argument is that universities internationalise to the detriment of teaching and learning quality.” The issue of student satisfaction is taken up by another recent study, this time from Ali Karakas at Turkey’s Mehmet Akif Ersoy University. It explores the perspective of English-taught students in Turkey, and, in particular, their satisfaction with the quality of teaching they received. Based on student surveys and interviews at a private English-medium institution in Ankara, Mr Karakas concludes that, “most students were pleased with their teachers’ linguistic competence and subject-matter expertise as well as [their institution].” He adds, however, that some issues with respect to language instruction were observed, including the level of instruction and the quality of learning materials. “One practical implication of these findings,” he says, “is that the EMI institution(s) should take an action to integrate a more academic-English-based curriculum into their language support programmes rather than a general English skill-based curriculum, using materials which are fit-for-purpose.” For additional background, please see:
Most Recent
-
British Council says student recruitment to UK higher education will get a boost this year from South Asia and the “Trump effect” Read More
-
New Zealand expands post-study work opportunities for international students Read More
-
As Iran retaliates across the Middle East, schools close, students worry, and institutions reassess transnational education Read More
















