OECD: Number of degree-holders worldwide will reach 300 million by 2030
New research from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) highlights the dramatic increased investment in higher education around the world, and projects the number of university graduates will more than double between 2013 and 2030.
Benchmarking Higher Education System Performance is a wide-ranging study that explores the landscape for higher education – with a notable focus on participation, inputs, and outcomes – across the world’s largest and most developed economies.
“The share of young people achieving a higher education qualification has increased steadily in recent years,” says the report. “Across the OECD, the proportion of 25-34 year-olds with a higher education qualification is now larger than the proportion with upper secondary education only. Moreover, despite the growth in higher education attainment across the OECD in recent decades, the employment premium enjoyed by higher education graduates has remained steady. Young higher education graduates also attract a strong premium on earnings; on average bachelor’s graduates in the OECD earn one-third more, and master’s graduates close to two-thirds more, than those with upper secondary or post-secondary non-tertiary education.”
The economic imperatives that surround higher education are on full display in the report, which notes that economic development and success relies on the corresponding development of human capital – that is, on building “the knowledge, skills, competencies and other attributes embodied in individuals that are relevant to economic activity”. Higher education plays a critical role in this process and that explains in large part the continuing expansion of tertiary systems in many countries around the world, including within the massive Chinese and Indian economies.
“Apart from positive economic outcomes,” adds the OECD, “higher education graduates also tend to report more favourable social and health outcomes than those without a higher education qualification. They are less likely to report suffering from depression and more likely to report to be in good or excellent health, to volunteer, to indicate trust in others and to feel a sense of political [engagement and agency] than those with upper secondary or post-secondary non-tertiary education only.”
300 million on the horizon
Among OECD countries, the average rate of degree attainment among 25-to-34-year-olds is 44% (a figure that reaches above 50% in nine member states, including Canada, Japan and the United Kingdom).
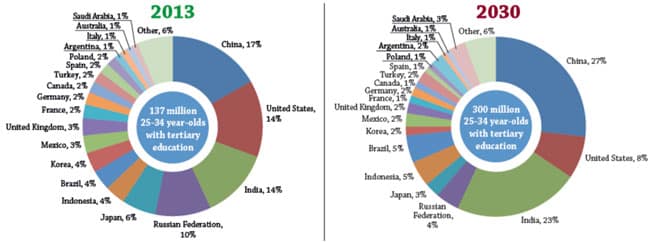
The International Association of Universities estimates there are now 18,000 degree-granting institutions in 180 countries worldwide. Looking across OECD and G20 countries, the OECD projects that this expanding field of colleges and universities will graduate many more students by the end of the next decade. More specifically, the number of 25-34 year-olds with a university degree is forecast to grow from 137 million as of 2013 to 300 million by 2030.
The following chart highlights this expansion along with the shifting distribution of degree attainment by country. Within that base of 137 million degree-holders in 2013, for example, 17% were in China, 14% in the US, and 14% in India.
Looking ahead to 2030, we see a very different distribution projected with 27% expected to be in China and 23% in India. The US share of the global population of degree holders is projected to decline to 8% by that point.
Put another way, China and India together are forecast to be home to nearly half of world’s university graduates by 2030.
Speaking to University World News, Professor Mats Benner of the Lund University School of Economics and Management in Sweden observed that the OECD analysis, “Points at the shift in the global higher education and research system, with the continuous expansion of Asia and more modest growth in Europe and North America.
“The rise of Asia is not merely quantitative. Asia is leading the way in many areas of research and training, primarily in engineering.
“Europe, which possesses neither the globally leading universities of the United States nor the powerhouses of Asia, needs to capitalise on its strengths, inclusion, diversity, and history. This calls for a continued increase in investments and widened recruitment and participation in education.”
As we have noted elsewhere, the number of internationally mobile degree-seeking students has grown from just over two million in 1999 to more than five million as of 2016. This represents an average annual growth rate of 5% among OECD members and 6% for non-OECD countries.
For additional background, please see:


















