Japan eases border restrictions but international students not prioritised for entry
- Japan will raise the daily cap on foreign arrivals from 3,500 to 5,000 beginning 1 March 2022, but international students will not be considered priorities for re-entry
- The decision to treat international students the same way as other permitted arrivals (businesspeople, interns, and Japanese residents and citizens) is a reversal of a November 2021 plan, which had prioritised their entry
- International students are taking to Twitter to voice their disappointment with this decision under the hashtags #allentriesarethesame and #educationisnottourism
- The education minister acknowledged that it will take some time for a significant proportion of the 150,000 visa-holding students stranded outside the country to be able to make it to Japan
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida has announced that on 1 March 2022, Japan will open its borders to allow 5,000 travellers per day into the country. The prime minster told the press that this “the first step in our gradual easing of the restrictions” and that the decision is based on expert opinion that the Omicron variant’s impact in Japan peaked in early February and is now on the decline.
Currently the entry cap is 3,500 travellers per day.
No special category for international students
While the news is – to a certain degree – encouraging, only a small proportion of the estimated 150,000 foreign students with visas to enter Japan will be able to return anytime soon, since the government will not prioritise foreign students in the new 5,000-per-day cap. They will be treated in the same way as businesspeople, technical interns, and Japanese citizens/residents. This means that it will take some time before a significant volume of foreign students will be able to resume or begin studies in Japan. Japan's Education Minister Suematsu Shinsuke acknowledged in a press briefing that “more time will likely pass before all the students can enter Japan.”
In terms of who will be able to enter Japan the soonest, it will be those with the earliest confirmed flight reservations rather than any particular category of traveller. Even residents of Japan will not be treated differently than other travellers.
A disappointing feature of the new border policies for international students is that the date on students' Certificate of Eligibility – one of the documents required to obtain a study visa – will not be considered in officials’ determination of who is permitted to enter Japan the soonest. Back in November 2021, international students had been singled out as one of the groups that would be prioritised for entry and their Certificate of Eligibility date was to be used by immigration officials to determine when they could enter. The November plan to prioritise international students for entry was scrapped soon after because of the spread of the Omicron variant, which also led to the tightening up again of Japan’s borders.
A January 2020 survey conducted by Davide Rossi, owner of the agency GoGo World and founder of the site EducationIsNotTourism.com, found that nearly half (46%) of more than 3,000 student respondents who had wanted to study in Japan decided to switch to another country for their studies. The expansion of the arrival cap to 5,000 travellers, with no prioritisation of international students, is unlikely to encourage many students to believe they can count on beginning studies in Japan any time soon or according to any predictable time frame.
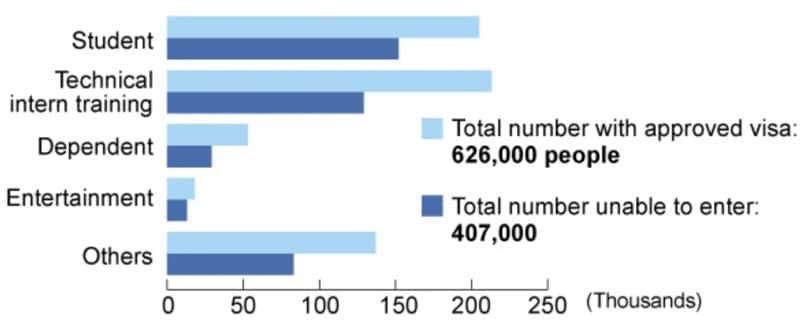
As illustrated in the chart below, international students are among the largest categories of people with valid visas who have been unable to enter Japan during the pandemic.
Rules around quarantine
Travellers who have received COVID booster shots will not be required to quarantine upon arrival if they are coming from countries that are considered to have an acceptably low number of COVID cases. If they are coming from what are deemed “high-risk” countries in terms of their epidemiological situation, boostered travellers will need to quarantine at home for three days.
Other travellers (who have not received their booster shot) will be required to quarantine for 7 days (either at home or at an approved hotel), though a negative test on day 3 will allow them to end their self-isolation. Non-boostered travellers from high-risk countries will be required to spend the first three days of quarantine at a designated hotel.
Still too strict according to many
When announcing the slightly eased border restrictions on 17 February, Prime Minister Kishida acknowledged that his COVID policies regarding arrivals are still the strictest of the G7 countries. His decision to retain a highly cautious approach to controlling borders comes despite the World Health Organization recommending that countries relax border restrictions or remove them completely.
International students are taking to Twitter with the hashtag #allentriesarethesame to protest the announcement that they will not be prioritised when borders begin to ease in Japan. Another hashtag in use is #educationisnottourism. Tourists will remain unable to enter Japan even after 1 March.
Last week, an education and science committee set up by Japan’s Liberal Democratic Party drafted a resolution calling on the government to prioritise the re-entry of international students, saying that “Japan is losing its international value” as a study abroad destination.
Why aren’t border restrictions being eased further?
Prime Minister Kishida’s overall stance towards COVID – including tight restrictions affecting individuals and businesses across the country – is partly due to the fact that Japan’s health system is still overburdened by Omicron cases because only public or “major” hospitals are able to treat COVID patients. In addition, the prime minister has been criticised for a relatively slow COVID booster rollout in Japan. In early February, less than 10% of the population had received their third doses of a vaccine.
For additional background, please see:
Most Recent
-
British Council says student recruitment to UK higher education will get a boost this year from South Asia and the “Trump effect” Read More
-
New Zealand expands post-study work opportunities for international students Read More
-
As Iran retaliates across the Middle East, schools close, students worry, and institutions reassess transnational education Read More
















