Sweeping new rules ban for-profit school tutoring in China
- The Chinese government has introduced a package of new regulations that effectively ban for-profit tutoring for any subjects included in the country’s core school curriculum
- The move has rocked the fast-growing edtech sector, and especially any providers of online tutoring services
The Chinese government has introduced sweeping regulations intended to curb online and private tutoring operations in the country. The move has rocked the edtech sector in China and abroad, and access to the massive Chinese market is now going to be very different for service and technology providers in this space. The private tutoring industry in China is valued at US$120 billion and has grown to be a very lucrative sector for Chinese and global investors alike in recent years.
In essence, companies that provide tutoring services around academic subjects in China’s National Curriculum for the years of compulsory schooling – such as math, science and history – are no longer allowed to make profits, raise capital through stock markets, or go public. Companies that currently offer such tutoring through a for-profit business model must switch to a non-profit organisation in order to be permitted to continue operations. It appears, however, that companies providing private tutoring to adults may not be affected by the new rules.
Most seriously for foreign firms and Chinese firms delivering services via a foreign affiliate, overseas investment in online and private tutoring operations for school-aged children is no longer permitted. Also forbidden is any curriculum-based tutoring of compulsory subjects that happens during vacations or weekends, as well as any teaching of foreign curriculums and any hiring of foreign instructors operating outside of China.
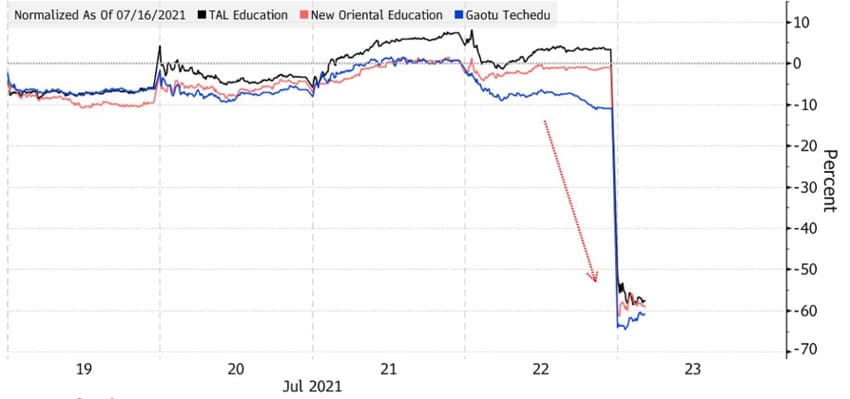
The impact of the announcement has sent edtech stocks into a deep plunge, as illustrated in the chart below.
Major companies and investors are being affected, including New Oriental Education & Technology Group, Koolearn Technology Holding Ltd., TAL Education Group, Gaotu Techedu Inc, Tiger Global Management, Temasek Holdings Pte, and SoftBank Group Corp.
The new regulations have already had an operational impact on some firms. One prominent example is VIPKid, an online tutoring service based in Beijing and backed by Tencent Holdings. VIPKid engages native English-speaking tutors in the US and Canada to provide video tutoring services to students in China. The company has already said that it will immediately stop selling classes taught by foreign tutors and will otherwise take steps to comply with the new rules.
What are the reasons for the new regulations?
The government has declared that the new regulations are aimed at:
- Stopping education operations from putting profits ahead of the welfare of students. One-on-one private tutoring fees are often about US$200 an hour.
- Reducing financial pressure on middle- and upper-middle-class families that are contributing to low birth rates (i.e., because having more children is obviously more expensive). In May, China announced that parents can now have up to three children. Previously the cap had been two children.
- Alleviating the anxiety of parents and children who face incredible competition in school and the economy – there is even a term, Jiwa, which means “chicken baby” that as Reuters notes, “refers to children pumped with extracurricular classes and energy-boosting ‘chicken blood’ by anxious parents.”
- Private tutoring is often seen as the best way to help students pass tough gaokao exams.
The Ministry of Education alleges that the tutoring and private education industry in the country has been “severely hijacked by capital,” and that this development “broke the nature of education as welfare.” The intention going forward is to place more onus on, and investment into, the Chinese school system to educate China’s children.
Story is still developing
It is not yet clear how rigorously enforced the new rules will be, as tutoring providers in China play a key role in helping students to succeed at school, and later, in fuelling the Chinese labour force. Reuters reports that,
“More than 75% of students aged from around 6 to 18 in China attended after-school tutoring classes in 2016, according to the most recent figures from the Chinese Society of Education, and anecdotal evidence suggests that percentage has risen.”
At this stage, the government rather vaguely says that companies violating the new rules will have to take “corrective measures.” If the crackdown on private tutoring ends up being rigorously enforced, some analysts envision a 70%+ revenue drop for major players in the K-12 private tutoring space.
Another agenda?
US-based media outlet Foreign Policy speculates that the new regulations are “part of growing xenophobia in China,” saying that,
“The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) spends a lot of time worrying about ideological education. Measures restricting the study of US and world history, for example, were put in place years ago. As the CCP sees it, banning foreign curricula and foreign teachers could prevent the creeping influence of foreign ideas and discourage Chinese students from applying to overseas universities.”
At the same time, Foreign Policy notes, “The regulations are not going to stop the very rich, who often have Ivy League ambitions for their children, from seeking out foreign tutoring anyway through discreet personal contacts and US bank accounts.”
For additional background, please see:
Most Recent
-
British Council says student recruitment to UK higher education will get a boost this year from South Asia and the “Trump effect” Read More
-
New Zealand expands post-study work opportunities for international students Read More
-
As Iran retaliates across the Middle East, schools close, students worry, and institutions reassess transnational education Read More
















