New analysis projects strong growth in global language learning with digital a key driver
- A new global market evaluation projects strong growth in both offline and online language learning through 2025
- Digital learning will be a key driver over this period with the global market expected to triple in size over the next five years
New analysis from the global market intelligence platform HolonIQ projects a "U-shaped recovery" for offline and blended language learning through 2025. But the forecast also anticipates that direct-to-consumer digital language learning services will triple in growth over this same period.
"Digital Language Learning is accelerating rapidly, increasing access, reducing cost, and leveraging technology to drive higher levels of language proficiency at scale," says HolonIQ. "Beyond tens of millions of new 'mobile first' language learners, digital is serving a much needed on-ramp and enabler for both online and offline tutoring."
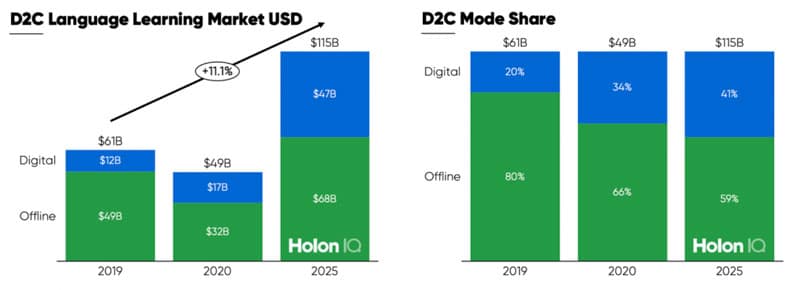
The HolonIQ analysis argues that the total language learning market is "materially under-estimated" due to the fragmented nature of offline provision in combination with strong recent-year growth in digital delivery. Using a combination of demand side and supply side inputs, the HolonIQ model projects a global language training market of US$115 billion by 2025, up from an estimated US$61 billion as of 2019. "We estimate the language learning market will almost double in size by 2025," notes the analysis. "Mobile-first and online tutoring will accelerate and triple in size over the next five years."
To underscore that point, the following charts illustrate that projected growth will be heavily influenced by the expansion of digital delivery, which is expected to account for more than 40% of industry revenues by 2025.
HolonIQ projects that students pursuing English language studies will in turn be the primary drivers of growth in both offline/blended and digital delivery, as reflected in the additional charts below.
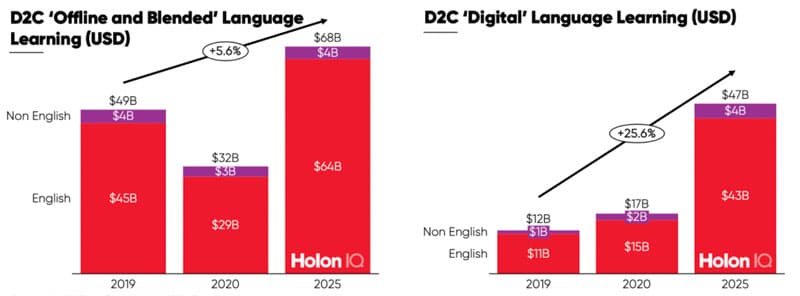
"We have fundamentally upgraded our outlook," says HolonIQ. "This may seem counter-intuitive given the widespread damage to offline and in-person providers COVID has driven, however we are optimistic on the mid to long-term economic recovery and remain convinced of the long-term demand for ‘blended’ in-person, campus-based and generally ‘face to face’ and ‘peer-to-peer’ English language learning. As hard as it is to imagine right now, under a positive recovery scenario, we see demand for offline language learning exceeding 2019 levels by 2024 and regaining ground rapidly, albeit having undergone a digital transformation to protect against another disruption."
There are some intriguing aspects of this analysis, including that the broader market is notoriously difficult to measure (especially with respect to new and emerging digital offerings), and the persistent and growing role of digital delivery going forward.
Based on our historical understanding of the composition of the global language travel market, it is possible that the HolonIQ projections overstate the proportion of English language learning within the total market. But the trends we often observe in this respect reflect only those students that travel for language study, and we can acknowledge that that represents only a fraction (i.e., less than 1%) of all language learners worldwide.
HolonIQ estimates the total population of language learners worldwide at roughly 1.8 billion, of which slightly more than 1.4 billion seek to learn English for work, study, or pleasure.
For additional background, please see:
















