China continues to show its strength in global rankings
- The latest major ranking release shows Chinese universities trending steadily upward within the top 100 to 200-ranked institutions worldwide
- Some observers believe the relative financial stability of Chinese institutions during and after the pandemic will accelerate further improvements in ranking performance in the years ahead
The 2021 edition of the Times Higher Education World University Rankings is just the latest indication of the continuing rise of Chinese higher education.
This year's ranking contains few surprises at the top of the table: the University of Oxford has claimed the #1 ranking for the fifth straight year, and eight other places in the top ten are held by leading US universities, including Stanford, Harvard, and MIT.
But the real story again this year is what we see outside of that elite group. US universities outside of the top 200 are losing ground in the global rankings over time whereas Chinese institutions are on the ascent.
The headline is that China's Tsinghua University is the first Asian institution to break into the top 20 in the THE ranking. But the number of Chinese institutions in the top 100 also doubled, from three last year to six this year. And all but one of the top 20 ranked Chinese institutions has improved its standing in the 2021 table.
The broad pattern observed in this year's results is available at a glance in the following chart. It shows how Chinese (in red) and American (in yellow) institutions in the 200-300 rankings band are trending over the last six years.
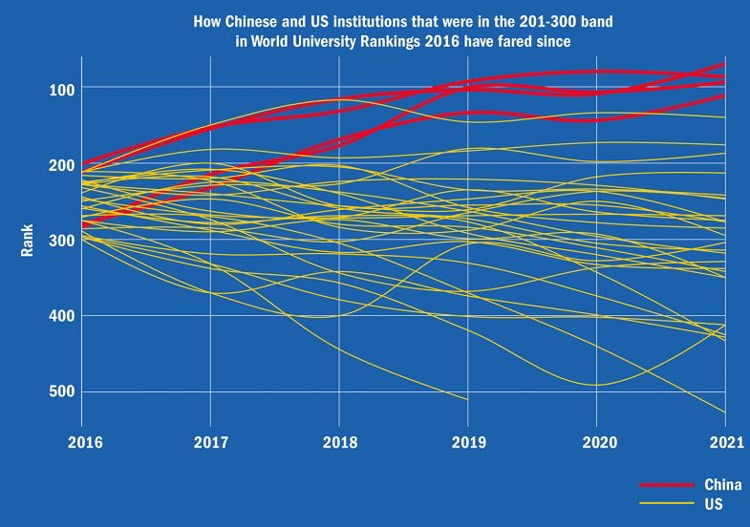
A related analysis from Times Higher Education points out that, "Chinese universities have also been closing the gap with the US on citation impact since the 2018 edition, and this year the research quality of the middle-ranking universities in the two countries – based on the number of citations achieved by the middle 50% of ranked universities – is beginning to converge for the first time. This means that some middle-ranking Chinese universities are now outperforming some middle-ranking US universities."
Looking ahead, the future prospects of each country's higher education institutions may now hinge in part on their relative financial stability. In this regard, Chinese institutions are once again operating from a position of strength. The Chinese government has invested heavily in higher education for decades now, with additional funding targeted to top tier institutions with the goal of seeing them ranked among the top universities globally.
In comparison, the pandemic has left some US institutions in a more precarious financial position with reductions in public funding and tuition income leading to staff reductions. This could in turn affect research output and rankings in the years ahead.
A recent analysis from Brookings assesses risk factors around major funding sources for US institutions, including public funding and tuition revenues, and puts the current situation in stark terms: "Nearly every school is at least at some risk of significant financial losses...The risks are incredibly different at different schools. Many schools face difficulties. If things turn out really bad, some schools face closures."
A further bit of data crunching from THE points out that a number of institutions currently in the top 200 may be particularly vulnerable to a downturn in international student numbers. "[The data suggests] that several universities in the UK in particular could suffer from a drop in international student traffic, alongside a smaller number of institutions from other anglophone nations such as Canada, the US and Australia."
Times Higher Education relies on two data sets from the global rankings for these conclusions. The first measures the scale of international student intakes at a university; the second assesses institutional income. Those universities with higher pre-COVID foreign enrolments, but lower income levels overall, are seen to be especially vulnerable to an enrolment downturn simply because they rely on those international revenues to a greater extent.
For additional background, please see:
















