US: COVID-19 impacts include campus closures and recruiting challenges
- A growing number of US colleges are forgoing in-person modes of teaching and learning, turning as much as possible to online courses to help their students continue on their study paths
- International students who must usually take most classes in-person to maintain visa status will soon be allowed to take more online classes
- A recent snap survey shows that three-quarters of US institutions are worried about their ability to recruit Chinese students
- The same survey shows that relatively few Chinese students were absent from US campuses at the time that the US introduced restrictions on travelers from China
In California, New York, and Washington – the US states where the largest number of COVID-19 cases have been reported – some colleges have closed their campuses and/or shifted to online classes for the rest of the semester so as to minimise the spread of the virus among students and the wider community. Part of the thinking here is to adhere to the expert advice to maintain “social distancing” (i.e., staying several feet away from other people and avoiding large gatherings).
Elite universities moving to online provision
Stanford University, MIT, and Harvard University have suspended in-person classes and have moved (or are in the process of moving) classes online. Other campus closures include the University of Washington, Lake Washington Institute of Technology, and several other colleges in the Seattle area. Most recently, closures have expanded to New York state and other regions of the country as well.
Changes to visa rules pending
Because international students are normally required to take almost all classes in person to maintain their visa status, there are plans to relax this rule and move to a protocol where colleges will submit a form detailing adaptations in place for international students to complete their courses online. Homeland Security’s Student and Exchange Visitor Programme (SEVP) spokesperson Carissa Cutrell said that “more details will be provided to SEVIS users [in mid-March].”
Worries about yield
Of course, it isn’t just current international students who are a concern for US colleges and universities; it’s also prospective students, who now, because of COVID-19, can’t be reached using traditional in-person methods such as visits to target countries and school fairs. For this reason, many colleges are working hard on their remote recruitment strategies, including providing more online content about their schools and programmes, hosting webcasts, and working with agents and partners abroad.
Survey highlights commitment to students
In February 2020, the Institute of International Education (IIE) conducted a snap survey of institutional representatives from 234 US institutions to learn more about how US colleges were coping with the travel ban currently in place on Chinese students coming into the US. The survey was conducted between 13–16 February and informs a recently released report entitled COVID-19 Effects on U.S. Higher Education Campuses.
Currently one in three international students in the US is Chinese (totalling 369,550 in 2018/19), highlighting the particular risk posed to colleges and universities in the country as a result of travel restrictions to as well as from China.
Importantly, the institutions surveyed by IIE host nearly half (47%) of all Chinese students in the US, and 19 in 20 of the most popular institutions for Chinese students were represented among the respondents.
A relatively small number affected by travel ban
Relatively few surveyed universities (87, or 37% of the total) reported cases of Chinese students having been unable to return to campus; only 831 Chinese students had been unable to return to campus at the time of the survey. The vast majority had either not gone back to China for their holidays or had returned before the travel ban came into effect. In fact, the 831 students unable to return to study in the US represent just 0.4% of the total population of Chinese students at the US institutions surveyed.
Institutions are trying to offer strong supports
The survey found a high degree of involvement and concern on the part of institutions that did have students unable to return to campus, with many offering comprehensive supports for these students and options for them to keep working on their courses remotely. One hundred percent had been in touch with the affected students, and 94% had adopted a comprehensive support approach spread across faculty, academic advisors, and other departments.
In addition, reports IIE:
“40% of institutions specifically indicated they were working with students who were finishing their degree to ensure that they would be able complete their degree. Institutions often indicated a strong commitment to supporting students affected by travel restrictions. In several cases, institutions were creating customised measures for a single student to help them continue with their coursework.”
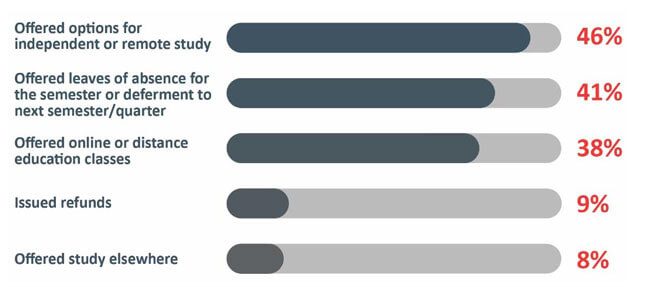
The following table shows the total proportions of institutions offering options for remote study, leaves of absence or the option to defer start dates, or online learning options. Less than 10% had offered full refunds.
Recruitment interrupted
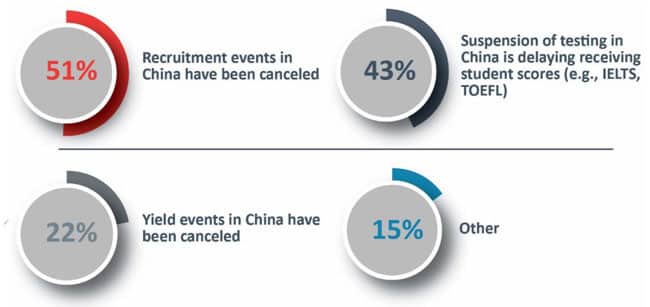
More than three-quarters of survey respondents said their recruitment activities in China had been negatively affected by the multifaceted effects of the virus. Half (51%) said that recruitment events in China had been cancelled and 43% said that the suspension of testing (such as IELTS or TOEFL) was delaying receiving student scores.
With traditional recruitment activities disrupted, institutions are relying more heavily on measures such as:
- “Offering virtual communications, webinars, and yield events;
- Working with in-country partners and agents on local recruitment;
- Offering online testing (Duolingo) instead of in-person testing such as IELTS;
- Dispensing with GRE requirements for the moment and considering GPA;
- Considering online submission of application and immigration documentation;
- Extending application deadlines for summer and fall 2020 semesters;
- Indicating options for students to enrolment until 2021.”
The survey also found that many US institutions have (American) students who had intended to study abroad, and that in most cases these students will “forgo their study plans.”
For additional background, please see:
















