Africa ascending: The demographic juggernaut driving student mobility in the 21st century
The following feature article marks the first instalment of a special series on emerging markets in Africa, and has been adapted for publication here from the 2019 edition of ICEF Insights magazine. The complete issue is available to download now.
Over the past decade, the massive youth populations of China, India, and other Asian nations have been the main forces driving an astronomic rise in international student mobility as students in these regions have left their countries to study for a better future. Most universities in Asia have, until recently, been unable to accommodate enough students and/or to provide students with a quality education.
But now, several Asian nations are rapidly expanding their higher education systems, offering students from the region an increasingly attractive array of options to study close to home. What’s more, demographics are changing in Asia, and by 2029, China’s population will begin to decline.
While Asia will remain a leading source of students for many years, the number of institutions – and countries – competing for students in that region is already increasing dramatically. As competition for Asian students intensifies, another region is quickly becoming a hotspot for the next wave of student mobility: Africa.
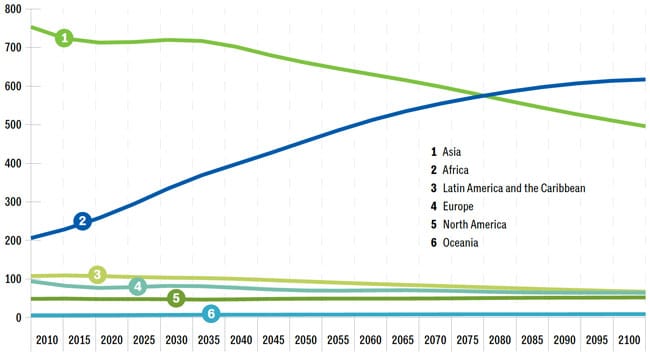
The number of students in sub-Saharan Africa leaving their countries for higher education is growing quickly, from 296,395 in 2012 to 374,425 in 2017, a 26% increase. The college-aged populations in African countries are huge already, and they are going to get much bigger, and soon.
“Africa is the new China, population-wise,” Adina Lav, assistant provost for international enrolment at George Washington University, said earlier this year in an interview for NAFSA’s International Educator magazine. In 2030, one of every four people aged 15–24 will live in Africa, according to the United Nations. This fact is ushering in a spike in demand for study abroad that will only get more intense.
China is now #2
France has historically been – and remains – the largest destination market for African students (especially from North and West Africa); it enrols more than 150,000 African students annually. In second place? It was once the UK and the US, but China has surpassed them. According to UNESCO figures, UK and US universities enrolled about 40,000 African students each in 2017, while Chinese higher education institutions hosted 50,000 in 2015. The number in China is now thought to be 60,000 – 20 times what it was in 2005. African engineering students are particularly drawn to Chinese programmes, which are often taught in English and are much less expensive than engineering programmes in the US or UK.
For years, China has been playing the long game, investing billions of dollars in infrastructure in African countries. The first Forum on China-Africa Cooperation was held in 2000, and since then Chinese capital in African markets has grown dramatically. Healthcare and education systems have been major beneficiaries. As one African student told the China Daily newspaper, “My country, as well as most others in Africa, lacks professional doctors. China is so developed in medicine and has helped my country a lot in building schools and hospitals. I appreciated that and thought it might be a good place to learn medicine.”
As this example suggests, China’s strategy for being the dominant foreign power in Africa and for recruiting students from the region goes something like this:
1. Chinese companies and government agencies set up operations in African countries and establish development projects such as schools, hospitals, and public infrastructure (e.g., port, bridges, roads).
2. The Chinese government offers tens of thousands of scholarships per year for African students to study in China, as well as lower tuition relative to Western institutions.
3. African students return home with a Chinese degree and/or Chinese language proficiency, ready to be employed in Chinese-owned companies in their country (or to pursue career opportunities in the world’s now-largest economy in China).
So far, the model seems to be working exceptionally well.
Up next in our series: a closer look at two of the most important growth markets in the region: Egypt and Ghana.
For additional background, please see:
















