Study reports declining international interest in US business schools
A new study from the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC) highlights the relative attractiveness of the business schools in leading study destinations. The framing of the study, Early Warning Signals: Winners and Losers in the Global Race for Talent, is very compelling. It looks at trends in international application volumes and related policy, but also takes a broader view in arguing that foreign enrolment trends in business schools are also an important indicator of how talent is moving around the world.
“Business schools are uniquely positioned to explain how mobility of talent connects to economic growth and vitality through our faculty research and expertise. However, as the developers of talent, we also have almost real-time data showing new trends in where talent is choosing to locate,” said Bill Boulding, chair of the GMAC Board and dean of Duke University’s Fuqua School of Business. “We feel it is critical we share this information now with policy makers around the world as talent will be the most important factor in determining who wins and loses economically in the future.”
The report examines trends around business school admissions in a number of countries but highlights the situation in the US in particular. There it finds that US business programmes have experienced a nearly 14% decline in international admissions applications this year. This is sharper decline than any other country in the world, and it stands in sharp contrast to the “largely rising or stable” applications volumes reported in many other destination countries. The report notes that increases in applications to business schools in Canada and Europe were largely driven by increases in international demand.
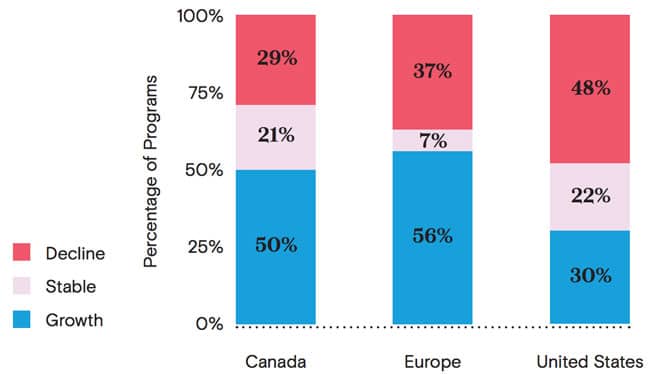
Canada has seen a surge in application volumes over the last three years, with seven in ten business schools reporting stable or increasing international application volumes again this year. The situation is similar in the UK where, even with some softening this year, roughly 70% of business schools have reported growing or stable application volumes over the last three years. In contrast in the US, roughly 20% of schools report stable numbers of international applications over 2017, 2018, and 2019, with only 30% reporting any increase.
The policy link
GMAC draws a very direct line between current immigration policy and the declining demand for US business schools. “Data from prospective applicants coupled with insights from business school deans point to a few key factors in the US decline – some newly emerging and some which have been developing over time, says the report. “Paramount are the changes to the H-1B visa cap, which have resulted in far fewer job opportunities for international students upon graduation and greater uncertainty about a future in the United States.” As we noted recently, the H-1B visa programme, through which foreign graduates may stay and work in the US for up to six years, has been subject to reforms under the current US administration. Recent data from US immigration reveals as well that H-1B applications are now coming under greater scrutiny by US officials.
Any such restrictions on the process or prospects for post-study work visas can be expected to have a chilling effect on foreign student interest and that appears to be exactly what GMAC has found in its analysis. The report says that, “For Indian students in particular, the ability to work and potentially settle for the long term in the United States is a primary reason for applying to US business schools. Two thirds agree that not being able to obtain a job in the United States post-graduation would prevent them from pursuing business school there (66%). The same was true for 52% of candidates from China.”
Lobbying ramps up
In a related development, a group of 50 business school deans from institutions throughout the US (along with 13 CEOs) published on open letter in the Wall Street Journal on 14 October. The letter appeals to President Donald Trump and other senior leaders in the US government for policy reforms, and it puts the situation bluntly.
“A combination of outdated laws, artificial regional and skills-based caps on immigration, and recent spikes in hostility are closing the door to the high-skilled immigrants our economy needs to thrive,” say the authors. “For the first time since we started keeping track of these data, the past three years have seen a reduction in the number of foreign students studying in America’s universities and business schools. Every year, we turn away hundreds of thousands of high-skilled immigrants for no other reason than that they failed to win the H-1B lottery.”
The letter calls for broad reforms to US immigration policy, and to the H-1B programme in particular. The GMAC report echoes this point and argues for both an increased number of H-1B visas to be issued each year, and for some professional fields to be exempt from the H-1B cap altogether.
“The United States must dramatically reform the H-1B process. Specifically, it should recognise that the country has industries with critical labor shortages where US citizens are highly unlikely to fill in the shortage in the near future [nb: the authors refer specifically to STEM fields elsewhere in the report]. Visa applicants applying for visas to work in those fields should not count toward the overall H-1B cap. That way, the US high-skill immigration system would be better aligned with the needs of the US economy.”
For additional background, please see:
Most Recent
-
British Council says student recruitment to UK higher education will get a boost this year from South Asia and the “Trump effect” Read More
-
New Zealand expands post-study work opportunities for international students Read More
-
As Iran retaliates across the Middle East, schools close, students worry, and institutions reassess transnational education Read More
















