Iran’s university enrolment is booming. Now what?
The population of Iran grew rapidly following the Islamic Revolution of 1979. It is estimated at about 80 million people today, with roughly 60% aged 30 or younger. For many years, the government has struggled to keep up with demand for education. The situation, however, began to reverse itself over the past decade or so.
As the following chart reflects, university enrolment in Iran began a period of very rapid expansion from about 2001 on. A recent item from The Washington Post notes, "Growth in the private and fee-based public sectors of higher education has been nothing short of astonishing, fuelled by the unprecedented expansion of distance-learning and part-time universities from just over 383,000 available spots in 2005 to 1.1 million in 2011. For the first time in Iran’s modern history, anyone who is willing to pay can go to university."

The other side of growth
There are two significant effects looming for both the rapid growth of Iran’s school-aged population and the dramatic expansion of higher education in the country. First, birth rates have slowed considerably following the population explosion in the period after 1979. The most recent data finds population growth of 1.29% in 2012 and forecasts indicate that growth will continue to slow until the country’s population plateaus around 105 million by 2050. These estimates are supported by more specific forecasts from the British Council projecting that Iran’s tertiary-aged population (that is, the population of 18-to-22 year-olds) will shrink by 2.1% through 2024. At the least, these projections illustrate that the rapid expansion of Iran’s school-aged population has stabilised, and the pool of college-aged students in the country will plateau and slightly contract over the next decade. At the same time, Iran is about to start producing very large numbers of university graduates. The Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs has estimated that as many as 4.5 million graduates will enter the labour market in the next few years. "The significance of this massive injection of additional educated job seekers is underscored by the fact that some 2.5 - 3 million working-age adult Iranians are already unemployed and looking for work," adds Mr Habibi. "The unusually large current student population in higher education indicates that in addition to the hundreds of thousands of high school graduates and less educated individuals who are expected to enter the job market each year, over the next four years, some 1-1.5 million university graduates will also enter the job market every year." The government will be naturally concerned about the political and social instability that could arise from such large numbers of unemployed or underemployed graduates. In fact, some observers argue that this concern has contributed to the rapid opening of Iran to greater international engagement and cooperation in recent years.
Postgraduate bottleneck
As the ready availability of a university education now leads to growing numbers of newly minted graduates in Iran, we can imagine that this may in turn spur demand for further studies at the postgraduate level. Particularly in the face of greater competition in an already tight job market - Iran’s economy continues to recover from a long period of international sanctions but has also been hit hard by the decline in world oil prices - students may look to advanced degrees as a natural source of advantage.
However, postgraduate capacity within the country is much more limited. The Washington Post reports, "Of the approximately 900,000 students who applied in 2011 for a master’s degree, only 60,000 were accepted, some 6%. The figures for PhD candidates were even worse: only 4% of those seeking a doctorate made it into a programme, a meager 6,000 students out of 127,000 applicants."
This supply-demand imbalance is likely a factor behind the British Council’s finding that Iran has been one of the fastest-growing outbound markets for postgraduate studies in recent years, and its corresponding projection of continued growth through 2024. In the five years between 2007 and 2012, the number of Iranian postgraduate students abroad grew from 8,000 to 17,000 (an average annual growth of 18%). Only Saudi Arabia - at an average of 25.3% per year and with the benefit of the world’s largest scholarship programme - grew more quickly during this period.
Looking ahead, British Council forecasts have it that outbound postgraduate mobility from Iran will reach 26,000 by 2024, for a projected average annual growth rate of 3.4% (from 2012 to 2024). "In 2024, the US is forecast to be the top destination of the six selected markets for Iranian postgraduates, of whom 11,900 will study in the US. Other strong postgraduate flows of Iranian students will be to Germany (5,700), Canada (2,800) and the UK (2,700). The strongest annual average growth rate will be seen in postgraduate student flows from Iran to the US (+4.3%), Germany (+3.6%), and Canada (+2.4%)."
The latest data from some of these destination countries suggests that these forecasts are well within reach already. New data from the Canadian Bureau for International Education (CBIE) reports 4,667 Iranian students enrolled in higher education in Canada in 2014 (representing, we should note, a year-over-year decline of 10% over 2013’s enrolment).
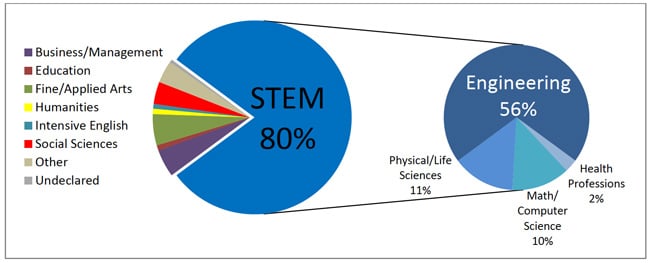
In the US, meanwhile, the latest Open Doors data from the Institute of International Education (IIE) finds a sixth consecutive year of growth for Iranian enrolment in 2014/15. There were 11,338 Iranian students in US higher education that year (an 11.2% increase over 2013/14). In a likely reflection of both the labour market and higher education capacity within Iran, 79% of those students were enrolled in postgraduate programmes and roughly 80% of those in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and math) subjects.